
What is an Aquaponics System and How Does it Work?
Aquaponics systems represent a revolutionary approach to sustainable farming. Combining aquaculture and hydroponics, these systems create a symbiotic environment. According to the Aquaponics Association, the market for aquaponics is projected to grow significantly, reaching $1.4 billion by 2025. This growth highlights the increasing interest in environmentally friendly food production methods.
Dr. Emily Green, an industry expert, emphasizes the potential of aquaponics. She states, "Aquaponics systems have the power to change how we think about food production." This sentiment resonates strongly in today's world, where food security is a pressing issue.
Yet, not all is perfect with aquaponics. Many systems face challenges, such as balancing fish and plant needs. The technology still requires refinement for broader adoption. Understanding these nuances is crucial for those interested in this innovative method. Acknowledging these imperfections can lead to better solutions and practices in aquaponics systems.
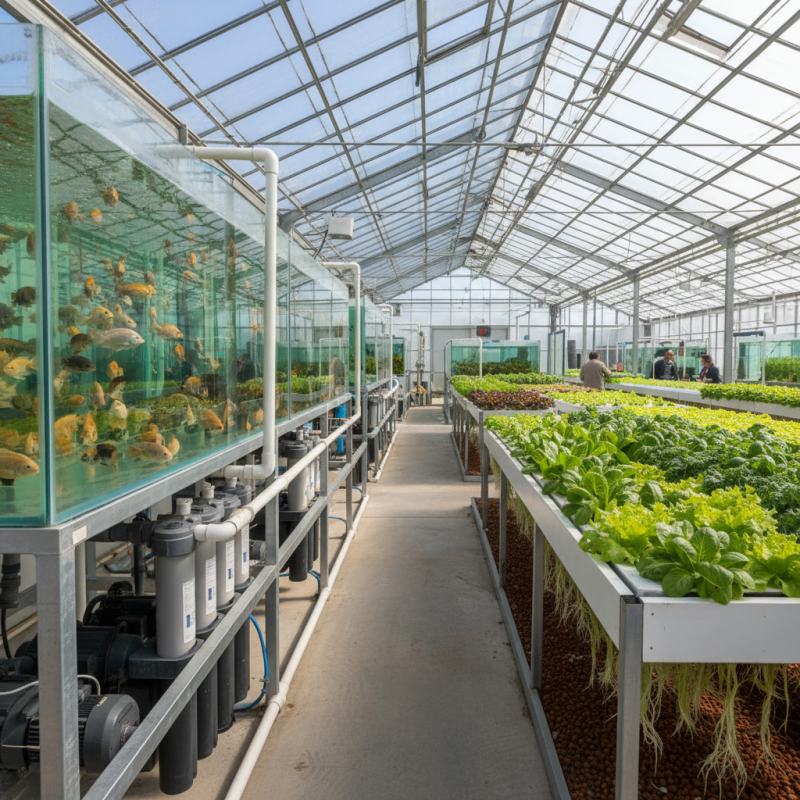

Definition and Overview of Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics is an innovative system combining aquaculture and hydroponics. It creates a symbiotic environment. Fish produce waste, which is rich in nutrients. This waste breaks down into compounds that plants can absorb. In return, plants filter the water, keeping it clean for fish. This natural cycle sustains both fish and plants.
Setting up an aquaponics system requires careful planning. Choosing the right fish is essential. Some fish are more resilient than others. They may tolerate varying conditions better. Additionally, not all plants thrive equally in this setup. It's crucial to research compatible species. Adjustments may sometimes be necessary. For instance, nutrient levels can fluctuate unexpectedly. Regular monitoring is key to a healthy system.
While aquaponics is promising, it can pose challenges. Maintaining balance can be intricate. Problems like algae overgrowth can arise. These issues might affect plant growth or fish health. Enthusiasts must be prepared for troubleshooting. Patience and observation are vital components of success. The learning curve can be steep, but the rewards are significant.
Key Components of an Aquaponics System
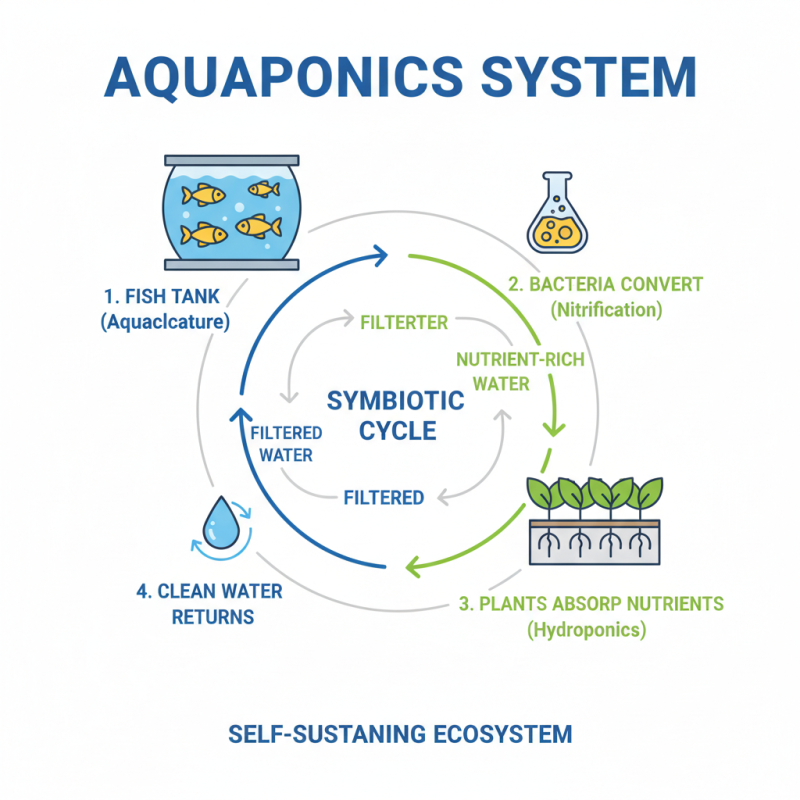
Aquaponics systems combine aquaculture and hydroponics. They rely on a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants. The fish provide waste, which is rich in nutrients. These nutrients are then converted by bacteria into forms usable by plants. This cycle creates a self-sustaining environment.
Key components include fish tanks, grow beds, and filtration systems. Fish tanks are crucial, housing the aquatic life that begins the cycle. Grow beds allow plants to take root and absorb nutrients. However, the balance between fish and plants may be tricky. Too many fish can overwhelm the system. On the other hand, too few fish can lead to nutrient deficiency for plants.
Filtration systems are vital for cleanliness. They ensure that the water remains healthy for both fish and plants. A deep water culture may be used to support plant roots. Regular monitoring is essential to maintain optimal conditions. Some may find this maintenance challenging. The success of an aquaponics system depends on careful attention to these components. Without diligence, it may not flourish as hoped.
The Process of Nutrient Cycling in Aquaponics
Aquaponics is a fascinating system that combines aquaculture and hydroponics. The nutrient cycling process is the heart of this method. Fish and plants create a symbiotic relationship. Waste produced by fish becomes a valuable nutrient source for plants.
In an aquaponics system, fish are raised in tanks. Their waste breaks down into ammonia. Beneficial bacteria convert ammonia into nitrites and then nitrates. These nitrates are what plants thrive on. The plants, in return, filter and purify the water for the fish, creating a clean environment.
However, maintaining the right balance can be tricky. Too much fish waste can overwhelm the system. Not enough plants may lead to poor water quality. Some growers struggle with the optimal fish-to-plant ratio. Constant monitoring is essential for success. This intricate balance is what makes aquaponics both rewarding and challenging.
Benefits of Using Aquaponics for Sustainable Agriculture

Aquaponics merges aquaculture with hydroponics. This method creates a cooperative system where fish waste becomes nutrients for plants. According to a 2022 report by the Food and Agriculture Organization, aquaponics can produce up to 10 times more food per square meter compared to traditional farming. It's a game-changer for urban agriculture, especially in areas with inadequate space.
One significant benefit of aquaponics is reduced water usage. It can save up to 90% of water compared to conventional agriculture. This efficiency is vital in a world facing severe water scarcity. Additionally, aquaponics systems can often be set up in small-scale operations, allowing for local food production. However, initial setup costs can be high. Some systems need daily monitoring of water quality and fish health, which can be daunting for beginners.
Experts emphasize the potential for aquaponics to support local economies. A 2021 study revealed that communities adopting aquaponics saw a 30% increase in local food security. Yet, challenges such as market access and technical know-how remain. Balancing these factors is crucial for maximizing the promise of sustainable agriculture through aquaponics.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Aquaponics Systems
Aquaponics systems combine fish farming and plant cultivation in a symbiotic environment. However, they come with common challenges. One major issue is balancing water quality. Fish produce waste, which can harm them if not managed. It's crucial to monitor ammonia and nitrite levels regularly. A simple test kit can help, but remember, consistent checks are key.
Another challenge is the choice of plants and fish. Not every species thrives together. Research compatible species that can coexist harmoniously. Consider local climate impacts as well. Some plants may require more light or temperature control than others. Experimenting with different combinations may lead to unexpected results. Documenting your process will help track what works best.
**Tips**: Maintain a regular feeding schedule for fish. Overfeeding can pollute the water quickly. Consider using aquaponics software for monitoring and managing your system. Adjustments will be necessary to optimize growth. Remember, mistakes are part of the learning process. Reflecting on them helps improve future yields.
Aquaponics System: Crop Yield vs. Water Usage
Related Posts
-

How to Minimize Repair Costs with Excellent After Sales Service for the Best Aquaponics System
-

Future of Aquaponics Systems Market Trends and Projections for 2025
-

Revolutionize Your Gardening: The Essential Guide to Building Your Own Aquaponics System
-

Leading the World in Aquaponics: Unveiling China's Best Export-Quality Systems
-

How to Successfully Maintain Your Aquaponics System for Optimal Growth
-

How to Build Your Own Sustainable Aquaponics System at Home
